MQTT communication between NodeMCU and Raspberry Pi
What is MQTT?
MQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol. MQTT stands for Message Queuing Telemetry Transport. Due to its lightweight nature, MQTT is widely used in IoT applications. Besides, MQTT supports bi-directional communication.
MQTT Architecture
MQTT is a publish/subscribe protocol. In this protocol, there are two types of entities: publishers and subscribers. Publishers publish messages to a topic. Subscribers subscribe to a topic and receive messages published to that topic. A topic is like a channel. A message published to a topic is received by all the subscribers subscribed to that topic.
To establish a connection between a publisher and a subscriber, a broker is required. The broker is a central entity that manages the communication between publishers and subscribers. The broker is responsible for routing messages to the correct subscribers.
Workflow
Send temperature data from NodeMCU to Raspberry Pi.
sequenceDiagram
autonumber
participant NodeMCU
participant Broker as MQTT Broker
participant RPi as Raspberry Pi
Note over Broker: Mosquitto MQTT Broker
Note over NodeMCU: Connected to DHT Sensor
NodeMCU->>Broker: Connect
RPi->>Broker: Connect
NodeMCU->>Broker: Subscribe to test/ctrl
RPi->>Broker: Subscribe to test/data
loop Every 5 seconds
NodeMCU->>NodeMCU: Read temperature from DHT sensor
NodeMCU->>Broker: Publish temperature to test/data
Broker->>RPi: Forward temperature data
endControl LED from Raspberry Pi using MQTT.
sequenceDiagram
autonumber
participant NodeMCU
participant Broker as MQTT Broker
participant RPi as Raspberry Pi
Note over Broker: Mosquitto MQTT Broker
NodeMCU->>Broker: Connect
RPi->>Broker: Connect
NodeMCU->>Broker: Subscribe to test/ctrl
RPi->>Broker: Subscribe to test/data
RPi->>Broker: Publish LED control command to test/ctrl
Broker->>NodeMCU: Forward LED control command
NodeMCU->>NodeMCU: Control LED based on received command
Note over NodeMCU: Turn LED on/offPrerequisites
Before we start, make sure you have the following:
- Raspberry Pi
- Any Linux distribution installed on your Raspberry Pi
- Python 3 installed on your Raspberry Pi
- NodeMCU
- DHT Sensor
Setup MQTT Broker on Raspberry Pi
In your Raspberry Pi, open the terminal and run the following commands to install Mosquitto MQTT broker:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeNow, install Mosquitto MQTT broker and the Mosquitto clients:
sudo apt install mosquitto mosquitto-clientsTo check if Mosquitto is installed successfully, run the following command:
mosquitto -vIf Mosquitto is installed successfully, you will see the following output:
16xxxxxxxxx: mosquitto version X.X.X starting
...
16xxxxxxxxx: Opening ipv4 listen socket on port 1883.
16xxxxxxxxx: Error: Address already in use
16xxxxxxxxx: Opening ipv6 listen socket on port 1883.
16xxxxxxxxx: Error: Address already in useThe above output shows that Mosquitto is installed successfully.
Now with this configuration, you can publish and subscribe to the MQTT broker from your Raspberry Pi. But, if you want to publish and subscribe to the MQTT broker from your NodeMCU, you need to configure the MQTT broker to accept connections from other devices.
To do this, edit the Mosquitto configuration file /etc/mosquitto/mosquitto.conf:
sudo nano /etc/mosquitto/mosquitto.confAdd the following lines to the configuration file:
listener 1883
allow_anonymous trueThe full configuration file will look like this:
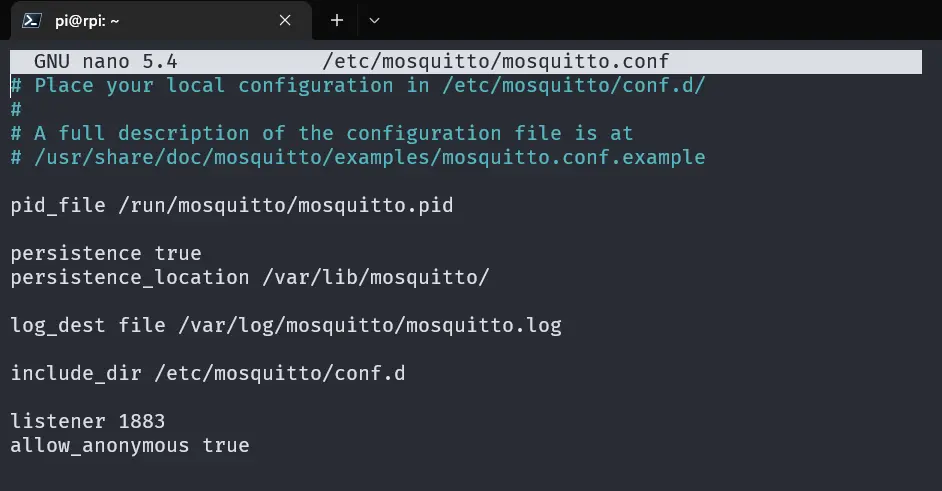
Save the file and restart the Mosquitto service:
sudo systemctl restart mosquittoNow, you can publish and subscribe to the MQTT broker from your NodeMCU.
Setup NodeMCU to Publish and Subscribe to MQTT Broker
We will write the program to publish and subscribe to the MQTT broker in C++. You can use Arduino IDE or any other IDE to write the program. Before we start, install the following libraries:
Now, connect the DHT11 sensor to your NodeMCU. The DHT11 sensor has three pins: VCC, GND, and DATA. Connect the VCC pin to the 3.3V pin of your NodeMCU. Connect the GND pin to the GND pin of your NodeMCU. Connect the DATA pin to the D6 pin of your NodeMCU.
Now, write the following program to publish the temperature data to the MQTT broker and subscribe to the MQTT broker to receive the LED control data:
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <DHT.h>
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <PubSubClient.h>
// constants
#define WIFI_SSID "xxxxxxxx"
#define WIFI_PASS "xxxxxxxx"
#define MQTT_SERVER "YOUR_RASPBERRY_PI_IP"
#define MQTT_PORT 1883
#define MQTT_PUB "test/data"
#define MQTT_SUB "test/ctrl"
// nodemcu pins
const int ledPin = LED_BUILTIN; // built-in led
const int dhtPin = 12; // D6
// global variables
unsigned long previousMillis = 0;
const long interval = 1000 * 5; // 5 second
// setup dht sensor
DHT dht(dhtPin, DHT11);
// utility functions
float getTemperature(int n) {
float sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum += dht.readTemperature();
}
return sum / n;
}
void setLedState(int state) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, state);
}
// setup wifi and mqtt
WiFiClient wifiClient;
PubSubClient mqttClient(wifiClient);
void reconnect() {
while (!mqttClient.connected()) {
Serial.print("Attempting MQTT connection...");
if (mqttClient.connect("ESP8266Client")) {
Serial.println("connected");
mqttClient.subscribe(MQTT_SUB);
} else {
Serial.print("failed, rc=");
Serial.print(mqttClient.state());
Serial.println(" try again in 5 seconds");
delay(5000);
}
}
}
void callback(char* topic, byte* payload, unsigned int length) {
Serial.print("Message arrived [");
Serial.print(topic);
Serial.print("] ");
String message = "";
for (int i = 0; i < (int)length; i++) {
message += (char)payload[i];
}
Serial.println(message);
if (String(topic) == MQTT_SUB) {
if (message == "on") {
setLedState(HIGH);
} else if (message == "off") {
setLedState(LOW);
}
}
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
// set pin modes
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(dhtPin, INPUT);
// connect to wifi
WiFi.begin(WIFI_SSID, WIFI_PASS);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
// connect to mqtt
mqttClient.setServer(MQTT_SERVER, MQTT_PORT);
mqttClient.setCallback(callback);
}
void loop() {
if (!mqttClient.connected()) {
reconnect();
}
unsigned long currentMillis = millis();
if (currentMillis - previousMillis >= interval) {
previousMillis = currentMillis;
float temperature = getTemperature(10);
Serial.println(temperature);
String message = String(temperature);
mqttClient.publish(MQTT_PUB, message.c_str());
}
mqttClient.loop();
}Now upload the program to your NodeMCU. You can use the Arduino IDE to upload the program. After uploading the program, open the serial monitor and check if the program is working correctly. You should see the temperature data being published to the MQTT broker.
Publish and Subscribe to MQTT Broker from Raspberry Pi
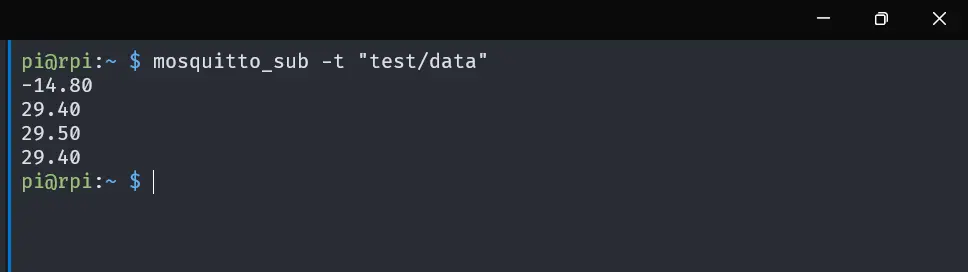
In your Raspberry Pi terminal, write the following commands to subscribe to test/data topic to receive the temperature data from the NodeMCU:
mosquitto_sub -t test/dataThis will subscribe to the test/data topic and print the temperature data received from the NodeMCU in the terminal in every 5 seconds.
Now, write the following command to publish the LED control data to the test/ctrl topic:
mosquitto_pub -t test/ctrl -m "on"This will send the on message to the test/ctrl topic. Now, the NodeMCU will turn on the LED. You can also send the off message to turn off the LED.
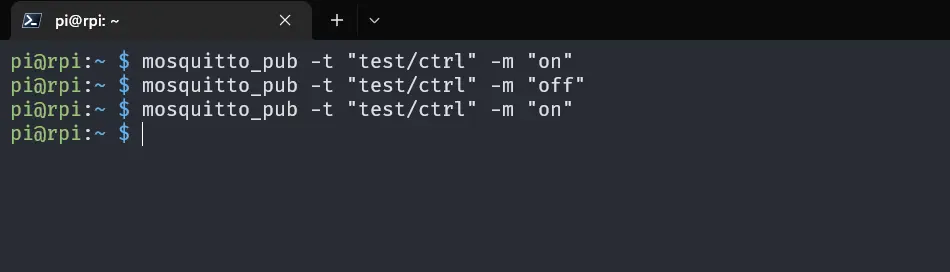
Note: with the above program, the LED will turn on when test/ctrl message is “off” and turn off when test/ctrl message is “on”. This is because the LED is build-in to the NodeMCU and it is active low.
References
- MQTT - The Standard for IoT Messaging, https://mqtt.org/.
- Eclipse Mosquitto, https://mosquitto.org/.
- Ndungu, Francis. “Install Mosquitto MQTT Broker On Ubuntu 20.04 Server.” Vultr, 15 October 2021, https://www.vultr.com/docs/install-mosquitto-mqtt-broker-on-ubuntu-20-04-server/.
- O’Leary, Nick. “knolleary/pubsubclient: A client library for the Arduino Ethernet Shield that provides support for MQTT.” GitHub, https://github.com/knolleary/pubsubclient.
- Santosh, Rui. “Install Mosquitto Broker Raspberry Pi.” Random Nerd Tutorials, https://randomnerdtutorials.com/how-to-install-mosquitto-broker-on-raspberry-pi/.